In observance of Deep Vein Thrombosis Awareness Month, let’s look at blood clots and their causes, risks, prevention, symptoms, and treatment.
What Is a Blood Clot?
A blood clot is a condition that happens when blood forms a solid mass in a vein or artery.
Blood clots can be helpful when they form to stop bleeding in response to a cut or injury. But when they form in your blood vessels without reason and don’t dissolve, they can cause problems that may require medical attention.
When blood clots form in deep veins within your body, they’re referred to as “deep vein thrombosis” (DVT). DVT occurs most commonly in the thigh, lower leg, or pelvis, but it can also occur in your upper body.
What Are the Risks of Blood Clots?
The biggest risk of blood clots is a pulmonary embolism (PE).
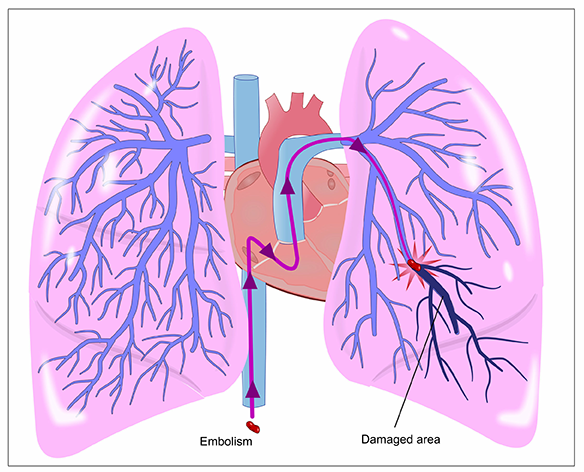
A pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot comes loose, moves through your bloodstream, and becomes lodged in your lungs. Depending on the size of the clot, it may cause damage to or even prevent blood flow to the lungs.
Either way, a pulmonary embolism is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate emergency intervention.
Deep vein thrombosis may also damage the vein’s valves, which causes long-term complications called post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS). Symptoms of PTS include discoloration, swelling, pain, and (in severe cases) ulcers. Either way, a pulmonary embolism is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate emergency intervention.
Can a Blood Clot Cause High Blood Pressure?
Deep vein thrombosis cannot directly cause high blood pressure. However, DVT can cause a pulmonary embolism, which can in turn cause high blood pressure in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension).
READ MORE: Surprising Causes of High Blood Pressure: Your Questions Answered
What Are the Causes of Blood Clots?
Conditions and lifestyle choices that can contribute to blood clots include the following:
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Prolonged inactivity
- Chronic medical conditions, such as heart disease and cancer
- Increased estrogen (for example, caused by pregnancy or birth control medication)
- History of vein injuries
- History of deep vein thrombosis
How Can I Prevent Blood Clots?
Blood clot prevention falls into three categories: moving, changing your lifestyle, and talking to your doctor.
Moving
Exercise and regular movement help prevent blood clots by keeping your blood moving through your veins and promoting vascular health. If you regularly sit for extended periods, try to move your legs or take a short walk every once in a while.
READ MORE: Best Exercise for Heart Health
Changing Your Lifestyle
Lifestyle changes can go a long way toward preventing blood clots. These are some of the healthiest lifestyle changes you can make:
- Quitting smoking
- Eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Checking your blood pressure regularly
Talking to Your Doctor
Do you have a family history, require a medical procedure, or take a medication that predisposes you to blood clots? Talk to your doctor about prevention methods that are appropriate for your unique medical situation.
What Are the Symptoms of Blood Clots?
You can watch out for a blood clot by being aware of its common signs and symptoms. However, approximately half of people diagnosed with blood clots don’t experience any symptoms.
So, it’s crucial to know the risk factors and discuss your health with your physician.
It’s also important to remember that blood clot symptoms are similar to cellulitis and peripheral vascular disease symptoms. As a result, your doctor will also consider known risk factors for these diseases, such as the following:
- Recent long travel
- Tobacco use
- Oral contraceptives
- Sedentary lifestyle
Symptoms of Blood Clots in the Legs
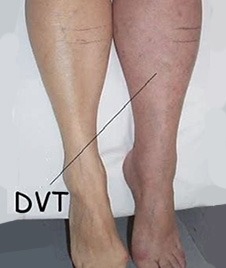
In the legs, symptoms of a blood clot include these indicators:
- Pain (especially in the calf or thigh)
- Swelling of the leg and veins
- Redness
- Skin that’s warm to the touch in the affected area
Keep in mind that symptoms will occur in only the affected leg — not both legs.
Symptoms of Blood Clots in the Arms

If you think you may have a blood clot in your upper body, look out for these indicators:
- Cramping
- Swelling
- Tenderness or pain
- Bluish or reddish skin discoloration
- Unexplained weakness
- Skin that’s warm to the touch
Symptoms of Abdominal Blood Clot
Abdominal blood clot symptoms include these indicators:
- Abdominal pain (severe or fluctuating)
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Bloating
- Diarrhea
- Blood in stool
- Fluid accumulation in the abdomen (ascites)
Symptoms of Blood Clots in the Heart

Symptoms of a blood clot in the heart — known as coronary thrombosis — include these indicators:
- Chest pain
- Pain in the ear, jaw, and head
- Pain that radiates down the left arm
- Dizziness
- Fainting
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Tightness around the throat
Coronary thrombosis can cause a heart attack or even cardiac arrest, causing your heart to stop beating. If you experience these symptoms, it’s crucial that you get to a local emergency room as soon as possible.
When To Go to the ER for a Blood Clot
Seek emergency care immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Coughing up bloody sputum (a mix of saliva and mucus)
- Rapid heartbeat
- Lightheadedness
- Difficulty or painful breathing
- Chest pain or tightness
- Pain that extends to the jaw, shoulder, back, or arm
- Sudden weakness or numbness in the arm, leg, or face
- Sudden difficulty understanding speech or speaking (aphasia)
- Sudden changes in vision
ER physicians will determine whether you’re experiencing a blood clot or another medical condition and provide emergency treatment.
For symptoms such as redness, swelling, and pain in an arm or leg, you do not need to seek emergency care. However, you should consult your doctor.
READ MORE: 10 Common ER Visits
Blood Clot Diagnosis
When you reach the emergency room, medical professionals will carry out these steps:
- Take your health and medication history.
- Ask detailed questions about your symptoms.
- Conduct a physical exam.
- Perform imaging.
Physicians typically diagnose deep vein thrombosis using an ultrasound, which allows them to view the veins and arteries. However, they can also order a blood test called the D-dimer test.
If your doctor suspects a pulmonary embolism, they’ll likely use a CT scan to diagnose it.
Emergency Blood Clot Treatment
Treatment for blood clots depends on the severity of your case.
If your doctor diagnoses you with a life-threatening blood clot, they may treat you with thrombolytics — often referred to as “clot busters.” Thrombolytics can rapidly break up blood clots. However, they also may cause sudden bleeding, so doctors reserve them for severe cases.
For blood clots that aren’t life-threatening, your doctor will prescribe an anticoagulant (a blood thinner). Anticoagulants prevent blood clots from growing and reduce your risk of developing additional clots.
If you can’t take either of the above drug types for medical reasons, your doctor may insert a filter into the vena cava (a large vein in your abdomen). The filter stops any clots that break loose from becoming lodged in your lungs (known as a pulmonary embolism).
Get 24/7 Care at Neighbors Emergency Center
At Neighbors Emergency Center, our staff can handle any and all emergencies, including deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolisms.
If you think you may have a blood clot — don’t wait. Visit your nearest Neighbors location for an evaluation.
