We all have this small, tubular organ attached to our large intestine called the appendix. While the jury is still out on what function the appendix serves in your body, you will find yourself in need of an emergency room urgently if it ever becomes inflamed (appendicitis).
Appendicitis is usually caused by an infection or an obstruction of the opening of the appendix from accumulated pieces of calcified stool. What results is abdominal pain and other symptoms that progress from dull to debilitating in a matter of hours or a couple of days (acute appendicitis). Without treatment, acute appendicitis can evolve into complicated appendicitis, where the appendix gets so inflamed that it bursts, spreading the infection throughout the abdomen and putting the body at risk of severe complications like sepsis, which can be fatal.
Appendicitis is very common, with nearly 250,000 people in the U.S. diagnosed annually. Though the risk of appendicitis peaks between ages 15 and 30, it can happen any time throughout life. It is also the top reason for abdominal surgery in kids, with 4 of every 1,000 kids undergoing an appendectomy procedure before the age of 14.
Appendicitis is something that will not go away without treatment, and it can develop into something serious, so it should always be treated as an emergency medical situation as soon as you recognize the symptoms. We’ve put together the vital information you need to know to decide when to go to the ER for appendicitis.

Signs and symptoms: What does appendicitis feel like?
Abdominal pain is the first sign of appendicitis, and it happens to be one of the main complaints bringing patients to emergency rooms. So how can we recognize if this abdominal pain is linked to appendicitis and not some other condition?
Here are some tell-tale signs to look out for:
- The pain is located on the lower right side of your abdomen
- The pain starts suddenly (it might awaken you from sleep)
- The pain begins as dull but becomes more sharp and severe over a short amount of time (4 to 48 hours)
- The pain is worse when you move around, breathe deeply, cough, or sneeze
- The pain is so severe that it limits your movement, causing you to bend in the middle or even curl up in the fetal position
While pain is often the first sign of appendicitis, other symptoms can follow, including:
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal bloating or a distended belly (especially in children younger than 2)
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
In children, these symptoms may present similarly to food poisoning or gastroenteritis, or even a mild stomach ache. If your child complains of stomach pain and starts experiencing any of the symptoms described above, take them to the ER as quickly as possible.

Should you go to urgent care or an ER for appendicitis?
Appendicitis should always be handled as if it is a life-threatening condition. Emergency rooms are equipped to properly diagnose and provide treatment for appendicitis, whether your case is acute or if your appendix ruptures. While an urgent care facility is a good place to go if you’re experiencing less severe abdominal pain, you should always go to an emergency room when experiencing appendicitis symptoms.
When to go to the ER for appendicitis
With appendicitis, symptoms can go from painful to potentially fatal if ignored or left untreated. In addition to the symptoms we described above, one red flag that should send you straight to an emergency room is if the typical lower right-side abdominal pain you’re experiencing turns into an excruciating pain that spreads all over the abdomen. This is a classic sign that your appendix has ruptured, and you should seek emergency medical care immediately.
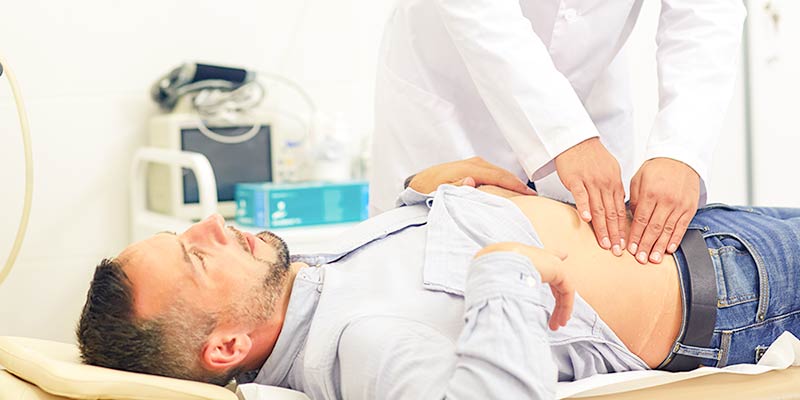
How do doctors diagnose appendicitis?
When you arrive at the ER, your doctor will ask about your medical history, symptoms, and then conduct a physical exam. Doctors will look for rigidity in the abdomen. They will apply pressure on the lower right quadrant of the abdomen and release it. If the pain feels worse after pressure is released, you likely have appendicitis.
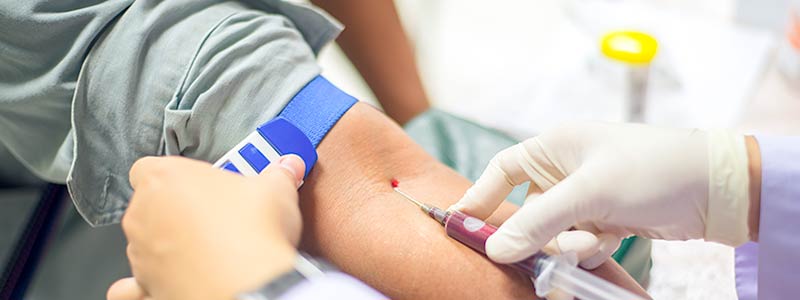
To confirm the diagnosis, doctors may also perform one or more of these tests:
- Urine: Urinalysis will rule out a urinary tract infection or kidney stone
- Blood: Blood test results with a high white blood cell count might indicate the presence of an infection
- Imaging: X-ray, ultrasound, CT or MRI scans can provide confirmation of appendicitis or find other sources of your abdominal pain

What is the treatment for appendicitis?
After the diagnosis has been confirmed, patients will receive antibiotics to treat the infection. In the end, the only effective treatment for acute appendicitis is an appendectomy, or surgery to remove the appendix.
An appendectomy can be done with minimal invasiveness through laparoscopic surgery, where a few small incisions are made in the abdomen and the surgeon uses a camera and surgical tools to remove the appendix. An appendectomy may also be performed as open surgery called a laparotomy, using one abdominal incision around 2 to 4 inches in length is made to remove the appendix. Open surgery takes longer to recover from than laparoscopic surgery, but it may be the best option depending on the patient’s medical history and symptoms.
If your appendix has burst, the same surgical options are available treatments, but they will also take time to clean your abdominal cavity to prevent more serious infection or sepsis. A ruptured appendix can sometimes result in the formation of a pocket of infection called an abscess, which will need to be drained completely before an appendectomy can be safely performed. Draining the abscess involves the insertion of a tube in the abdomen to drain the fluid. This process may take several weeks. Once the abscess is totally drained of fluid, and the inflammation is under control, the doctor will proceed with the appendectomy.
Head straight to Neighbors ER for appendicitis
When you’re in need of quick, thorough emergency care for appendicitis, your nearest Neighbors Emergency Center is here for you 24/7/365 with board-certified physicians and state-of-the-art imaging and laboratory services.